
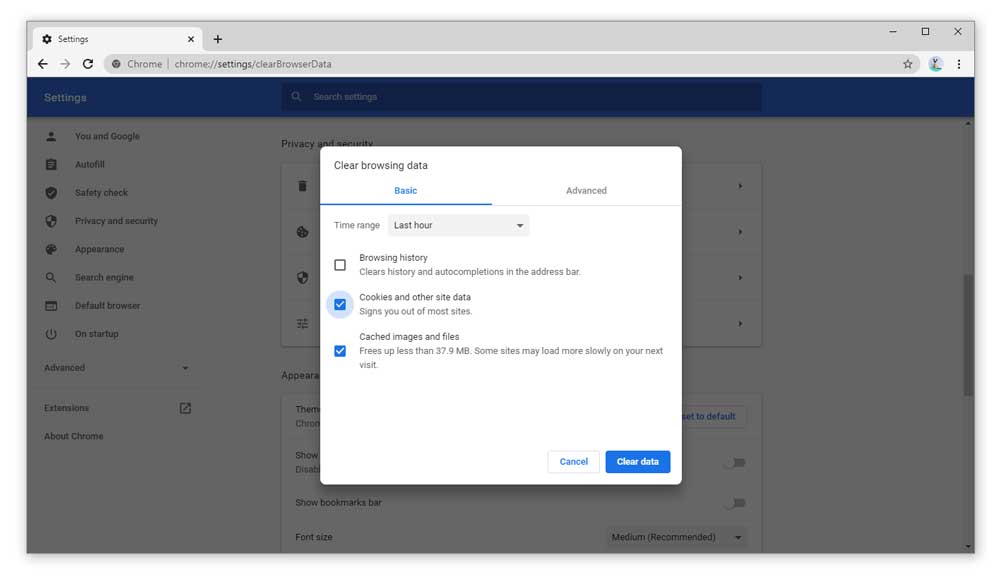

The two limits react differently to limits being reached: In this group,, and can aggregately use a maximum of 20% of the global limit. There's one group for each eTLD+1 domain. Each origin is part of a group (group of origins). There's also another limit called group limit - this is defined as 20% of the global limit, but it has a minimum of 10 MB and a maximum of 2 GB. There is no trimming effect put in place to delete parts of origins - deleting one database of an origin could cause problems with inconsistency. If this is exceeded, a process called origin eviction comes into play, deleting an entire origin's worth of data until the storage amount goes under the limit again. So if the free space on your hard drive is 500 GB, then the total storage for a browser is 250 GB. In Firefox, an internal browser tool called the Quota Manager keeps track of how much disk space each origin is using up, and deletes data if necessary. The global limit is calculated as 50% of free disk space. The maximum browser storage space is dynamic - it is based on your hard drive size. Storage is temporary by default developers can choose to use persistent storage for their sites using the StorageManager.persist() method available in the Storage API. Temporary data storage does not elicit any user prompts. In Firefox, when persistent storage is used, the user is given a UI popup to alert them that this data will persist, and asks if they are happy with that.

This will be evicted under a least recently used ( LRU policy) when Storage limits are reached.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
